GitOps Repository Structure¶
GitOps describes an approach to managing the deployment and maintenance of an environment through configuration stored in a Git repository. However, GitOps does not dictate a particular way the information in the Git repository is organized. There are a number of different tools and approaches available.
For the Toolkit, we had defined an opinionated approach to the GitOps repository structure to address complex deployments and take advantage of the capabilities of available GitOps tools. The following gives an overview of this opinionated GitOps repository structure.
App of Apps¶
There are two major types of resources in the repository:
- ArgoCD configuration
- Application "payloads"
ArgoCD configuration¶
In ArgoCD, collections of kubernetes resources that are deployed together are called "applications". Applications in ArgoCD are configured using a custom resource definition (CRD) in the cluster which means ArgoCD applications can deploy other ArgoCD applications (called the "App of Apps pattern"). With the "App of Apps pattern", the ArgoCD environment can be bootstrapped with an initial application. That initial bootstrap application can then be updated in the GitOps repository to configure other applications.
Application "payloads"¶
The ArgoCD configuration points to other paths within the GitOps repository (or various GitOps repositories) that contain the actual "payload" yaml to provision the applications (the deployments, config maps, etc that make up the applications)/
Layered components¶
In addition to separating the ArgoCD configuration from the application "payloads", the configuration has also been divided into three different "layers" of the cluster configuration:
- Infrastructure
- Shared services
- Applications
Infrastructure¶
Foundational elements within the cluster, like namespaces, service accounts, role-based access control, etc. These resources are often managed by the infrastructure team and are required by the other resources.
Shared Services¶
Shared services are application components that are used across multiple applications or across the cluster. Often these are operator-based services and managed independently from the applications.
Applications¶
The application layer contains the applications deployed to the cluster, using the infrastructure and shared service components.
Structure¶
Putting it all together, there are seven different locations for the GitOps content:
- Bootstrap
- Infrastructure ArgoCD configuration
- Shared services ArgoCD configuration
- Application ArgoCD configuration
- Infrastructure payload
- Shared services payload
- Application payload
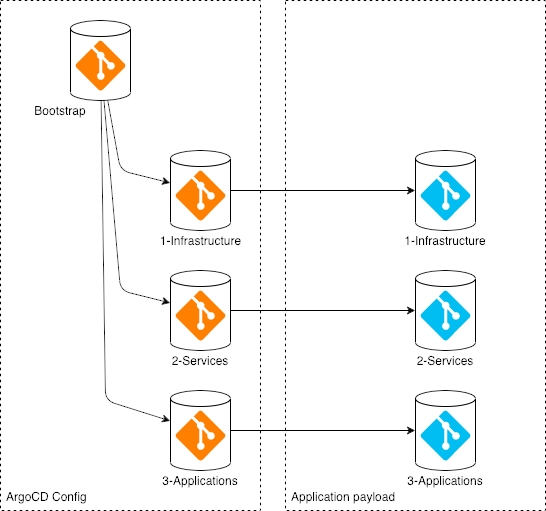
This repository implements a simple configuration where all seven collections of resources are stored in a single repository. For more complicated deployments, the resources can be separated into different repositories. For example, if the infrastructure, services, and application configuration is managed by different teams then each layer can be managed in a different gitops repository.
argocd/¶
The argocd/ folder contains the ArgoCD application config, separated into the different layer folders:
- 0-bootstrap
- 1-infrastructure
- 2-services
- 3-applications
The "bootstrap" repository must at least contain the argocd/0-bootstrap folder with the initial configuration. The other layer folders can either be defined in the same repository or separate repositories.
Multi-server¶
The GitOps repository structure supports defining the deployment configuration for multiple servers in a single Git repository. Each of the argocd configuration paths includes a cluster name/identifier so that the full path to the configuration is argocd/{layer}/cluster/{cluster id}, e.g. argocd/0-bootstrap/cluster/default. The default cluster id used is "default".
payload/¶
The payload/ folder contains the kubernetes resources for the application components for the infrastructure, services, and application layers. These folders can be in the bootstrap repository or any other repository.
config.yaml¶
In order to understand where all the pieces that make up the GitOps deployment can be located, the bootstrap repository contains a yaml file that defines the repository and path for each of the seven locations. This file can be used both by humans to understand the layout and by other tools to place content in the appropriate location. For example:
bootstrap:
argocd-config:
project: 0-bootstrap
repo: github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample
url: https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample.git
path: argocd/0-bootstrap
infrastructure:
argocd-config:
project: 1-infrastructure
repo: github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample
url: https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample.git
path: argocd/1-infrastructure
payload:
repo: github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample
url: https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample.git
path: payload/1-infrastructure
services:
argocd-config:
project: 2-services
repo: github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample
url: https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample.git
path: argocd/2-services
payload:
repo: github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample
url: https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample.git
path: payload/2-services
applications:
argocd-config:
project: 3-applications
repo: github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample
url: https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample.git
path: argocd/3-applications
payload:
repo: github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample
url: https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample.git
path: payload/3-applications
kubeseal_cert.pem¶
By default, the Toolkit uses Sealed Secrets to store encrypted credentials in the GitOps repository. Sealed Secrets works by installing the operator in the cluster and configuring it with a private key. Any credentials are encrypted with the corresponding public cert before storing the value in the GitOps repository. The operator then decrypts the credentials in-cluster and creates the relevant kubernetes Secrets.
In order to aid the process, the public certificate that can be used to encrypt additional secrets is stored in repository in the kubeseal_cert.pem.
Example¶
An example GitOps repository is provided at https://github.com/cloud-native-toolkit-test/gitops-sample